Homocysteine Support
Homocysteine Support contains synergistic nutrients to facilitate the efficient metabolism of homocysteine. Homocysteine is a natural compound produced by your cells, but high levels are linked to poor health. Homocysteine Support maintains a healthy methylation cycle, allowing for the normal production of its necessary and important...
Your Price: $45.00
 100% Satisfaction Guaranteed
100% Satisfaction Guaranteed  90-Day Money-Back Guarantee
90-Day Money-Back Guarantee  Made in USA
Made in USA

**New Stronger Formula**
- Supports healthy immune system function
- Supports ideal joint and cartilage structure
- Helps your nervous system to function properly
- Supports Optimal Methylation and Cardiovascular Health
- Supports Healthy Homocysteine Levels
- Increases Neurotransmitter Production
- Supports Primary Detoxification Pathways
- Promotes DNA Repair
Methylation is a vitamin-requiring biochemical process in the body that is critical for supporting many aspects of mental and physical health including regulating gene expression. Methylation occurs billions of times every second and helps the body to repair DNA on a continual basis. However, when methylation processes in the body slow down, an increase in the breakage of DNA strands can occur. In addition to maintaining DNA repair, methylation reactions help maintain optimal neurotransmitter production, homocysteine balance for cardiovascular health, and the recycling of molecules that are required for detoxification and healthy inflammatory response. Methylation is also required for proper energy metabolism, immune and nerve cell function. Proper methylation can be inhibited by nutrient deficiencies including folate, and B2, B6 and B12. Certain medications such as acetaminophen, aspirin, ibuprofen and oral contraceptives can also deplete blood levels of these crucial B vitamins.
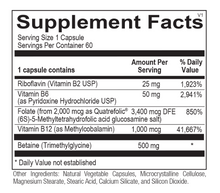
Homocysteine Support is a comprehensive formula that includes targeted amounts of five key nutrients designed to aggressively support methylation and homocysteine balance in the body. Homocysteine Support provides high-concentration folate as Quatrefolic® - 100% 5-MTHF, the biologically active form, and trimethyl glycine. The formula includes key methylation vitamins B2, B6 and B12 (methylcobalamin). This specific blend of methyl donors promotes DNA repair, homocysteine balance, neurotransmitter production, hormone balance and optimal detoxification.
Folate
Folate is a water soluble member of the B complex vitamins that is critical for maintaining optimal methylation. Folate is abundantly found in foods such as fruits and dark leafy vegetables but, can be easily destroyed by cooking or processing. The bioactive form of folate is 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF). 5-MTHF is required as a methyl group donor for several processes, including the production of mood regulating neurotransmitters, the synthesis of melatonin, and DNA production and repair.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 works with folate in many body processes, including the synthesis of DNA, red blood cells and supporting health of the myelin sheath, the insulating exterior that surrounds nerve cells. B12 is found primarily in animal foods. Vegetarians and the elderly run the highest risk of B12 deficiency. Methylcobalamin is the preferred form of B12, as it is the biologically active form of B12 and supports the up-regulation of methylation pathways.
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is a crucial B vitamin that is involved in the production of proteins in the body, neurotransmitters that help regulate mood, red blood cell formation and the proper functioning of the immune system. B6 is required for more than 60 different enzymatic reactions that occur in the body. Vitamin B6 works along with 5-MTHF and B12 in the recycling of homocysteine. B6 also supports a healthy cardiovascular system by promoting healthy platelet aggregation and aids in maintaining normal blood pressure.
Vitamin B2
Optimizing B2 status helps support healthy blood pressure, particularly in patients with genetic mutations (MTHFR 677 > T polymorphism).
Betaine (Trimethylglycine)
As a methyl donor, trimethylglycine supports liver function, including detoxification pathways. Trimethylglycine has been shown to be beneficial in protecting against fat accumulation in the liver, due to its lipotropic properties (donating a methyl group to aid in the transport of fat out of the liver). Trimethylglycine also works alongside B2, B6, B12 and folate in maintaining normal homocysteine levels.
Suggested Use:
1 capsule per day or as recommended by your health care professional
60 caps
Everything You Need
-

FREE SHIPPING
Orders Over $99 -

DOCTOR
CREATED
Products -

BEST PRICE
GUARANTEE
Lowest prices
from our website -

NO HASSLE
RETURNS -

US COMPANY
We’re in Arizona